The basics
Once you've created your user groups and put some users in them, you can begin to define for each of these user groups which parts of the catalog they will be able to see/edit.
Access rights on product information
Access rights enable you to configure the scope of the role and visibility of users to the product catalog in the PIM.
You can define access rights on three axes:
- Locales: If a product catalog is available in several locales, it is possible to define which locale can be viewed and/or edited for each user.
- Channels: If a product catalog is available in several channels, it is possible to define which channel can be viewed and/or edited for each user.
- Categories: If a product catalog uses the classification tree in the PIM, it is possible to define for each user which products can be viewed and/or edited, depending on the classification of products in the different categories.
- Attribute groups: If a product catalog uses the attribute group in the PIM system, it is possible to define for each user which attributes can be viewed and/or edited, depending on the attribute group in which they are positioned.
Hierarchy of access rights for product information
For each axis, there are three levels of access:
- Permission to edit information
- Permission to view information
- No rights: the information is hidden from the user
As rights are subject to 4 axes, hierarchy prevents conflicts defining permissions for each user. The axes of the hierarchy are the following:
- Channel
- Locale
- Category
- Attributes Group
- Category
- Locale
How do we apply the rule of hierarchy? To apply the rule to the child axis, at least one access right must be granted to view the parent axis.
Does this sound complex? Don't be afraid! Below are a couple of examples to illustrate how the rule of hierarchy applies to each user.
Example 1
A user has been granted the following rights:
- ecommerce channel: view right
- de_DE locale: no right
- Shoes category: view & edit permissions
- General attribute group: view & edit permissions
This user will never see the products in the Shoes category, nor edit the attributes in the General group in the de_DE locale because the user does not have access to this locale, and he will never be able to see it. He can only view, but not edit, values specific to the ecommerce channel.
Example 2
Now, let’s permit the same user to view the locale en_US:
- de_DE locale: no rights
- en_US locale: view permission
- Shoes category: view permission
- General attribute group: view & edit permissions
The user can see the products in the Shoes category and the attributes in the General group in the en_US locale, but cannot edit them because he has only a view permission for the en_US locale.
Example 3
Finally, let’s permit the same user to edit the locale fr_FR:
- de_DE locale: no rights
- en_US locale: view permission
- fr_FR locale: edit permission
- Shoes category: view & edit permissions
- General attribute group: view & edit permissions
On the fr_FR locale, the user can edit the products in the Shoes category and the attributes in the General group. He can only see products and their attributes in the en_US locale, and he can’t see de_DE product information.
Rights depending on the locale
For each user group, it is possible to define which locale the product information can be viewed and/or edited.
Three levels of access
There are three levels of access based on the locales. Each one is described in the sections below.
The edition rights
- In the product grid
- In the product edit form
- In the enriched categories' attributes
- In the Asset grid and asset page
- In the Reference entity records grid and record page
The user can also update product information for this specific locale by import or API.
The view right
Suppose a user has rights to only view information for a specific locale (ie, his user groups only have the Allowed to view product information permission). In that case, the particular channel will be displayed in the dropdown menu for the available locales:
- In the product grid
- In the product edit form
- In the enriched categories' attributes
- In the Asset grid and asset page
- In the Reference entity records grid and record page
The user won't be able to update product information for this specific locale by import or API. However, Information for this locale will still be editable for enriched categories, assets, and reference entity records.
No right
If a user has no rights to see or edit information for a specific locale, this locale will not be displayed in the dropdown menu of available locales:
- In the product grid
- In the product edit form
- In the enriched categories' attributes
- In the Asset grid and asset page
- In the Reference entity records grid and record page
He won't be able to edit product data in the product form or import product data for this specific locale. However, Information for this locale will still be editable for enriched categories, assets, and reference entity records.
Rights depending on the channel
For each user group, it is possible to define for which channel the product information can be viewed and/or edited.
Make sure your user role has the permission to manage channel permissions so you can define permissions for user groups.
Three levels of access
There are three levels of access based on the channels. Each one is described in the sections below.
The edition rights
- In the product grid
- In the product edit form
- In the enriched categories' attributes
- In the Asset grid and asset page
- In the Reference entity records grid and record page
The user can also update product information for this specific channel by import or API.
The view right
Suppose a user has rights to only view information for a specific channel (ie, his user groups only have the Allowed to view product information permission). In that case, the particular channel will be displayed in the dropdown menu for the available channel:
- In the product grid
- In the product edit form
- In the enriched categories' attributes
- In the Asset grid and asset page
- In the Reference entity records grid and record page
The user won't be able to update product information for this channel by import or API. However, Information for this channel will still be editable for enriched categories, assets, and reference entity records.
No right
If a user has no rights to see or edit information for a specific channel, this channel will not be displayed in the dropdown menu of available channels:
- In the product grid
- In the product edit form
- In the enriched categories' attributes
- In the Asset grid and asset page
- In the Reference entity records grid and record page
He won't be able to edit product data in the product form, nor import product data on this specific channel. However, Information for this channel will still be editable for enriched categories, assets, and reference entity records.
Set rights to user groups.
So now you better understand how the rights depending on the channels work, let's configure it in the interface:
- Go to Settings and select the Channels entry
- Select the channel
- Click on the Permissions tab
- Click in the fields to add user groups to grant them permissions
- Click on the Save button
Permissions are immediately applied to users.
An example
Julia is in the Horizon Home & Comfort user group, which has the right to edit product information regarding the Horizon Home & Comfort channel.
Robert is in the Horizon Outdoor & Adventure user group and only has the right to view product information regarding the Horizon Home & Comfort channel.
Mary is in the Translator user group and has no rights to product information regarding the Horizon Home & Comfort channel.

Rights depending on the categories
It is possible to define for each user group which products can be viewed, edited, and/or owned, depending on their classification in the categories.
Four levels of access rights
There are four levels of access you can grant for your user groups on each of your categories.
The owner right
If a user is the owner of the product information for the products that are in a given category (ie, his user groups have at least the Allowed to own products permission), he will be able to:
- View and edit the product information directly, rather than going through the proposal’s workflow
- View/review the current proposals for product values
- Approve/reject or partially approve proposals of values that need to be reviewed
- View/Change the product associations and categories
The edition rights
If a user has rights to only edit product information for the products that are in a given category (ie, his user groups have at least the Allowed to edit products permission), he will be able to:
- View the product information
- Create a product draft that will need to be approved by the product manager
- Generate/send a proposal that the product manager will process
To be able to access the Categories tab of the products that are in this given category, the user must be granted with the Consult the categories of a product role permission (System > Roles > Products > Consult the categories of a product). The user will be able to consult the categories but not edit them. Without this permission, the Categories tab won't appear.
The view right
If a user has rights to only view product information for the products that are in a given category (ie his user groups only have the Allowed to view products permission), he will only be able to view the product information and that's all. No possibility to edit it.
To be able to access the Categories tab of the products that are in this given category, the user must be granted with the Consult the categories of a product role permission (System > Roles > Products > Consult the categories of a product). The user will be able to consult the categories but not edit them. Without this permission, the Categories tab won't appear.
No right
If a user has no rights to see nor edit product information for the products that are in a given category, he won't be able to neither view nor edit the product information, whatever the screen in the PIM.
In the case a user has no rights to see nor edit product information for a given category, we hide this category in order to make the user interface even more simple.
If you remove the right to view the products on one given category, the PIM will automatically also remove its rights to edit and own the products on this category.
Same thing if you remove the right to edit the products on one given category, the PIM will automatically also remove its right to own the products on this category.
An example
Let's take several examples to make it clearer.
Julia is the product manager in her company. She is in the Audio manager user group.
Mary is an intern so she is in the Redactor user group.
Then we have Marco, the supplier. He is in the Supplier user group.
To finish, Elise is in the Clothes manager user group.
As you can see in the screenshot below, the Audio manager user group is owner of the products in the Audio and Video category, whereas the Redactor user group only has edit rights and the Supplier user group only has view rights. As it appears nowhere, the Clothes manager has no rights on the products of the Audio and Video category.
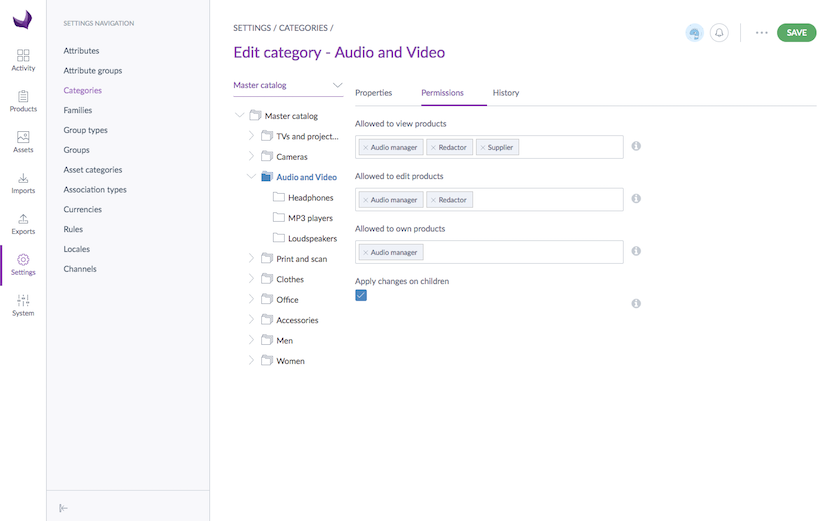
Now, let's imagine that the Sony SS-SP32FWB product is only categorized in the Audio and Video category. As a result of the application of these rights:
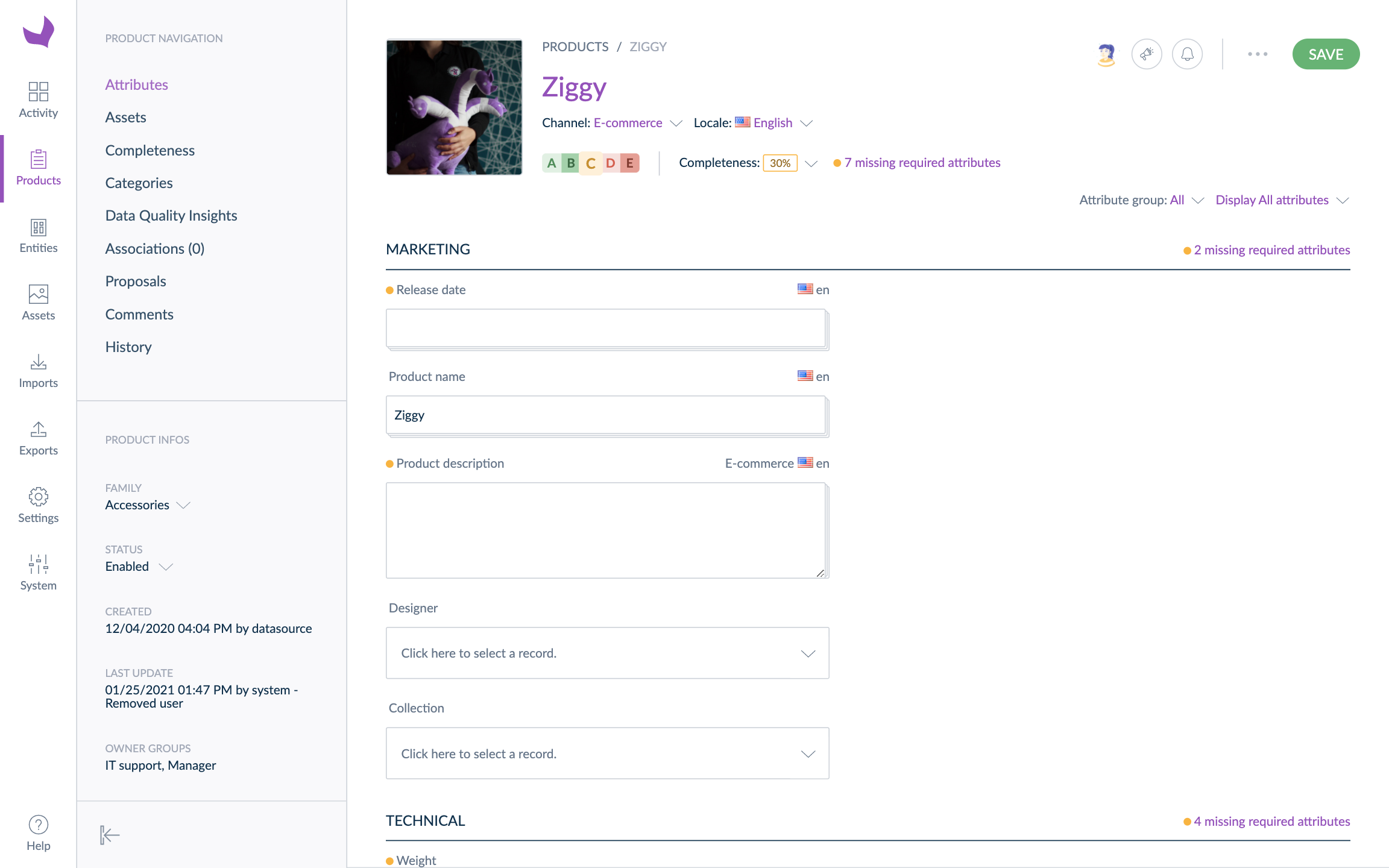
Julia will get the following product form for the Sony SS-SP32FWB product
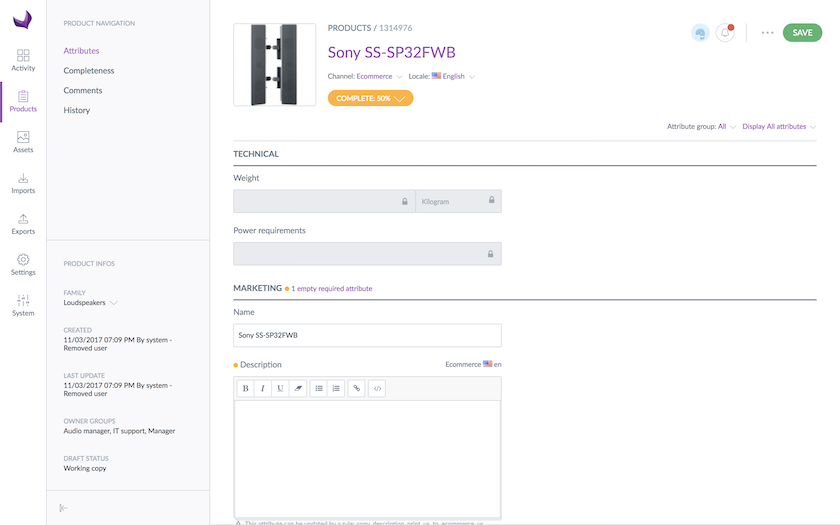
- Mary will get the following product form for the Sony SS-SP32FWB product. You can notice that the Categories, Associations and Proposals menu entries are hidden, in this case.
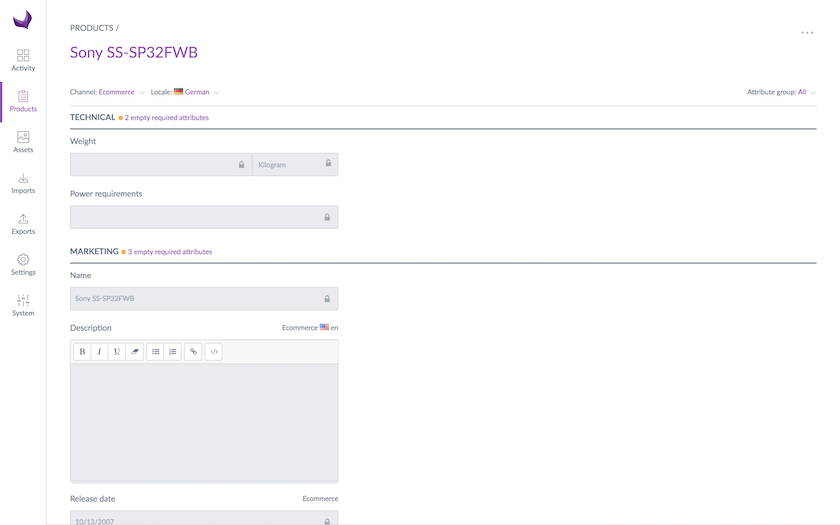
- Marco will get the following product form for the Sony SS-SP32FWB product. You can notice that the attributes values are greyed out because their edition is not allowed in this case.
- Elis won't be able to access the product form of the Sony SS-SP32FWB product. She won't even be able to view the Audio and Video category in the category tree.
Governance categories: Set extra permissions by Business Unit
Governance Categories overview
This feature answers the need to handle products across a business with multiple business units (muliple brands, multiple regions or even both). Governance Categories are designed to facilitate a more streamlined setup of permissions.
This feature will be useful for any customer who handles products in separate teams within their organisation, or has different product offerings by business-unit, without the need for multiple versions of their merchandising trees.
Governance categories are accessible to Premium customers only.
When should you use this feature?
Use this feature if you manage product information across different business units (teams or regions), each requiring unique access controls. It’s ideal for businesses handling sensitive or business unit-specific data.
You should mainly use this feature when you handle a high number of categories and you share some of them across business units but you need to separate which products can be seen by different teams in these shared categories.
Create a Governance Category tree
To create a governance category tree
- Enable the feature in System > Configuration
- Go to Settings > Categories
- Click on “Create tree”
- Select “Governance”
You can only create 1 governance category tree.
Note that ‘classic’ categories are now called merchandising and listed in a dedicated tab to differentiate them from governance categories.
Once the governance tree is created, you can add categories as you would for merchandising categories.
Set permissions to governance categories
After creating governance categories, you can assign user group permissions by category like explained in the previous chapter of this documentation.
About governance permissions
Governance category permissions work the same way as merchandising category permissions.
Let's take an example and imagine you have 2 business units managed by different teams
You could create a governance tree called “Brands” and 2 categories underneath with the following permissions.
| Category | User Group permissions | |
| AwesomeBrand | NewBrand | |
| AwesomeBrand | Edit rights (can edit products) | View rights (can view products but not edit them) |
| NewBrand | No rights (cannot see products) | Edit rights (can edit products) |
When a product is classified in one governance category, the permissions above will be applied to the user based on its user group.
In this example, you can make sure users from a specific brand have no or limited access to another brand's products, exactly like how merchandising category permissions work.
How governance permissions work with merchandising permissions
To make sure merchandising & governance apply, you have to make sure a product is classified in at least 2 categories: 1 merchandising category & 1 governance category.
When a product is classified in both a governance and merchandising category, the user is granted the strictest permission from both categories.
If a product is classified in a merchandising category where a user has edit rights and in a governance category where the same user has no rights, the user won't be able to see the product at all.
Same if a product is classified in a merchandising category where a user has no rights and in a governance category where the same user has edit rights, the user won't be able to see the product at all.
Example scenario
Let’s say you manage two brands (AwesomeBrand and NewBrand) with teams organized by product range (Tops and Accessories). You could create:
• One governance tree called Brands.
• One merchandising tree called Product Ranges.
• Four user groups: Tops AwesomeBrand, Accessories AwesomeBrand, Tops NewBrand, Accessories NewBrand.
Here is an example of possible permissions
| Category tree | Category | User group permissions | |||
| Tops AwesomeBrand | Accessories AwesomeBrand | Tops NewBrand | Accessories NewBrand | ||
| Brands | AwesomeBrand | Edit rights (can edit products) | Edit rights (can edit products) | View rights (can view products but not edit them) | View rights (can view products but not edit them) |
| Brands | NewBrand | No rights (cannot see products) | No rights (cannot see products) | Edit rights (can edit products) | Edit rights (can edit products) |
| Product ranges | Tops | Edit rights (can edit products) | No rights (cannot see products) | Edit rights (can edit products) | No rights (cannot see products) |
| Product ranges | Accessories | No rights (cannot see products) | Edit rights (can edit products) | No rights (cannot see products) | Edit rights (can edit products) |
What will be the result for products classified in these categories for each user group:
| Product | Categories | User groups | |||
| Tops AwesomeBrand | Accessories AwesomeBrand | Tops NewBrand | Accessories NewBrand | ||
| Product#1 | AwesomeBrand & Tops | Can Edit | Can't view | Can view | Can't view |
| Product#2 | NewBrand & Accessories | Can't view | Can't view | Can't view | Can Edit |
| Product#3 | Tops (no governance category) | Can Edit | Can't view | Can Edit | Can't view |
Example visualisation depending on the user
Here is another example of what products users could see within the same merchandising category.
- Full catalog view as an admin

Whereas if you were assigned as a Brand Manager, you may see one of the following views depending on your user group assignment:


The product catalog still exists in its entirety, and an admin can access all products, but there is a streamlined view for the brand managers of Ziggy Fashion and Ziggy Home.
Users can only view and export products classified in governance categories they have permission to access.
Key Limitations and Tips
- Category Tree Type: Once created, a merchandising category tree cannot be converted into a governance category tree, and vice versa.
- Filtering Limitations: It is not possible to filter on both a merchandising tree and a governance tree simultaneously within the grid or with export profiles.
-
Filtering with API: If you need to filter on both a merchandising and a governance tree in API requests, you have 2 options:
- filtering with 2 categories like this
{{url}}/api/rest/v1/products?search={"categories":[{"operator":"IN","value":["GovernanceCategory1"]}]}&search={"categories":[{"operator":"IN","value":["MerchandisingCategory1"]}]}&with_count=true - creating an API user with specific permissions on governance categories, then applying merchandising category filters within the API call
- filtering with 2 categories like this
Set rights to user groups
So now you better understand how the rights depending on the categories work, let's configure it in the interface:
- Go to Settings and select the Categories entry
- Select the category to set permissions on
- Go under the Permissions tab
- Click in the fields to add users groups to grant them permissions
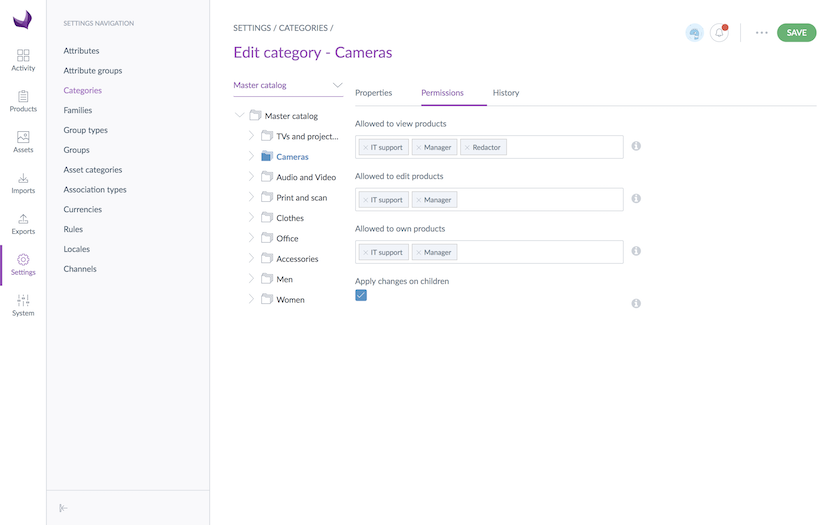
- Click on the Save button
Permissions are immediately applied to users.
By default, all users are entitled to all the rights on the created asset categories through the All user group, which is the user group by default. If you define permissions to specific groups, remove the All user group.
Some crucial tips
One product, several categories
If a product is in multiple categories of one tree or more, the most permissive right is applied to the product.
Example
The product A is categorized into:
- the Divided brand category, on which the Divided supplier user group has an owner right
- the Tshirt category, on which the Divided supplier user group only has an edit right
- the Yellow category, on which the Divided supplier user group only has a view right
Now, imagine Mary is in the Divider supplier user group. She will have the owner right on the product A.
One product, no category
If a product is not categorized at all, by default, all the users in the PIM will have an owner right on this product.
One user, several user groups
If a user is in several user groups, the most permissive right is applied to the product.
Also, if a user's User Group has no permissions on the Product Category, but the default “All” User group has Own permissions on this Product Category, then the user automatically benefits from the full access to the product.
The product A is categorized in the Tshirt category, on which:
- the Divided supplier user group has an owner right
- the Manager user group only has a view right
Now, imagine Mary is both in the Divider supplier and the Manager user groups. She will have the owner right on the product A.
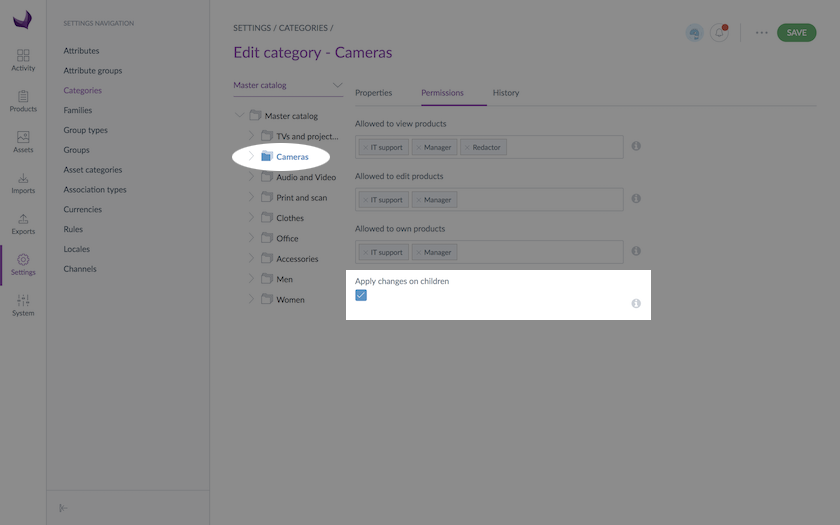
The “apply changes on children” option
The Permissions tab has an option called Apply changes on children. This option is checked by default. It means the permissions you granted to your current category will be applied to all its sub-categories.
As you can see in the example below, the Apply changes on children is checked for the parent category. So, all its sub-categories will get exactly the same user groups' configuration for the view and edit rights.
Rights depending on the attribute groups
It is possible to define for each user group, which attribute values of products can be viewed and/or edited, depending on their attribute groups.
Three levels of access
There are three levels of access based on the attribute groups. Each one is described in the sections below.
The edition right
If a user has rights to edit product information for a specific attribute group (ie, his user groups have at least the Allowed to edit attribute permission):
- In the product form, the values of all the attributes of the group are enabled, and they can be edited
- When using a product import, the values of all the attributes of the group can be updated
- When exporting products, the values of all attributes of the group will be exported
The view right
If a user has rights to only view product information for a specific attribute group (ie, his user groups only have the Allowed to view attribute permission):
- In the product form, the values of all the attributes of the group are disabled, and they can't be edited
- When using a product import, the values of all attributes of the group cannot be updated
- When exporting products, the values of all attributes of the group will be exported
No right
If a user has no rights to see nor edit product information for a specific attribute group:
- In the product form, the values of all the attributes of the group are not shown, so they can't be edited
- When using a product import, the values of all attributes of the group cannot be updated
- When exporting products, the values of all attributes of the group won't be exported
- The views using the attribute groups (columns or filters) are not displayed in the list of views.
An example
Let's take an example with the following user groups permissions configuration regarding the Marketing attribute group.
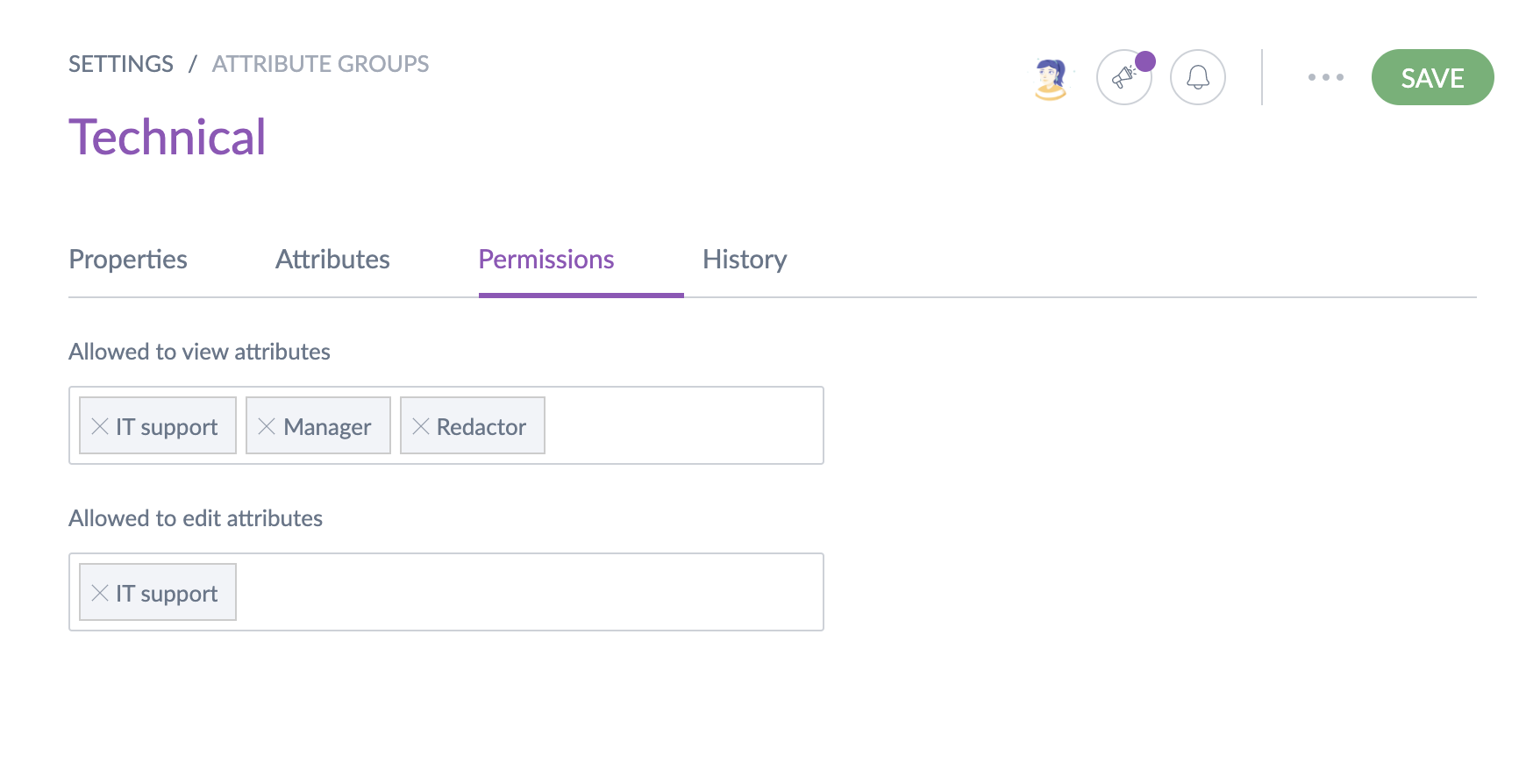
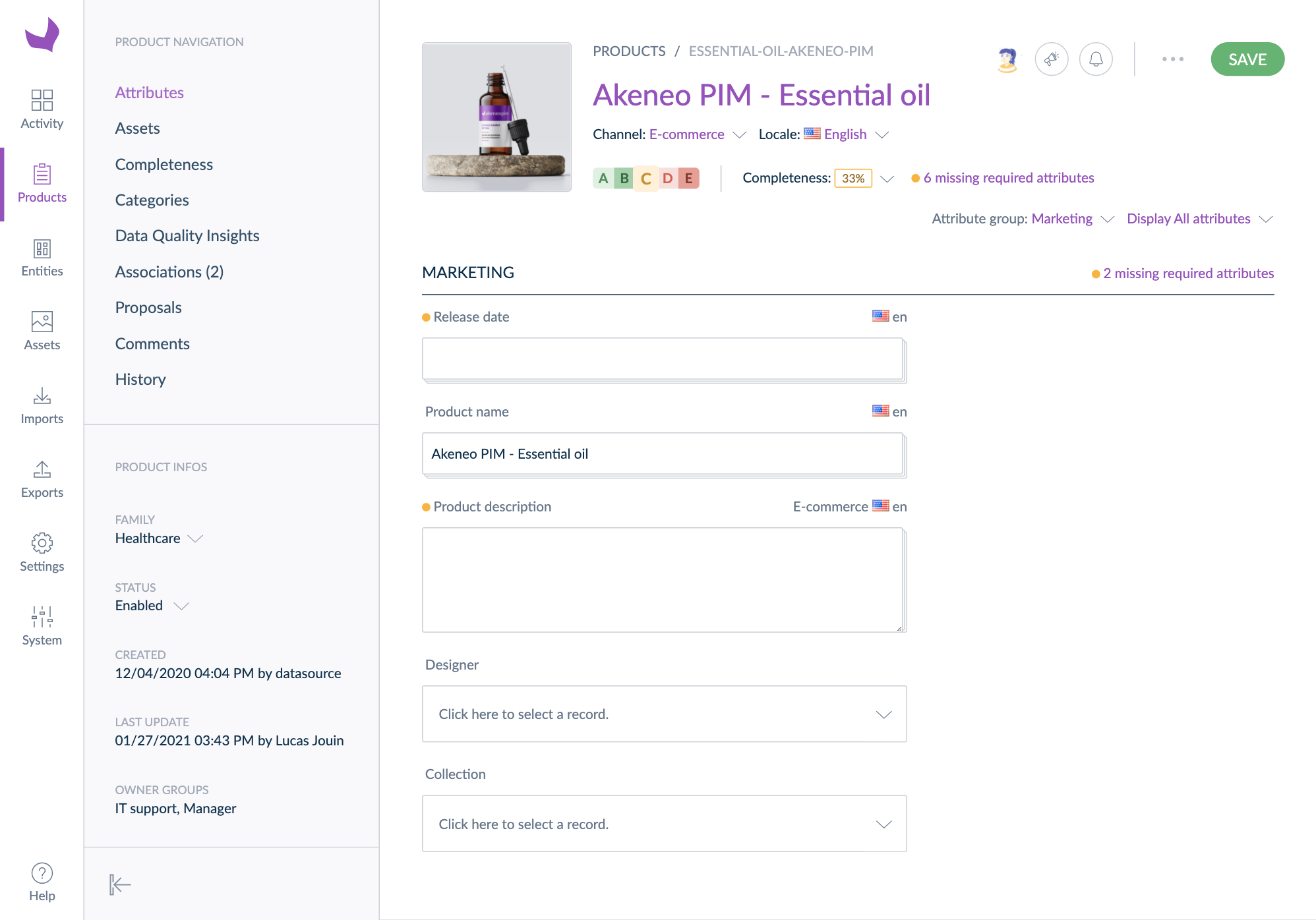
Julia is in the Marketing user group that has the right to edit product information regarding the Marketing attribute group. As a result, in the product form, she can view/edit the product information in this attribute group as you can see in the screenshot below.
Robert is in the Intern user group that only has the right to view product information regarding the Marketing attribute group. As a result, in the product form, he can only view the product information in this attribute group as you can see in the screenshot below. The attributes in this attribute group are greyed out.
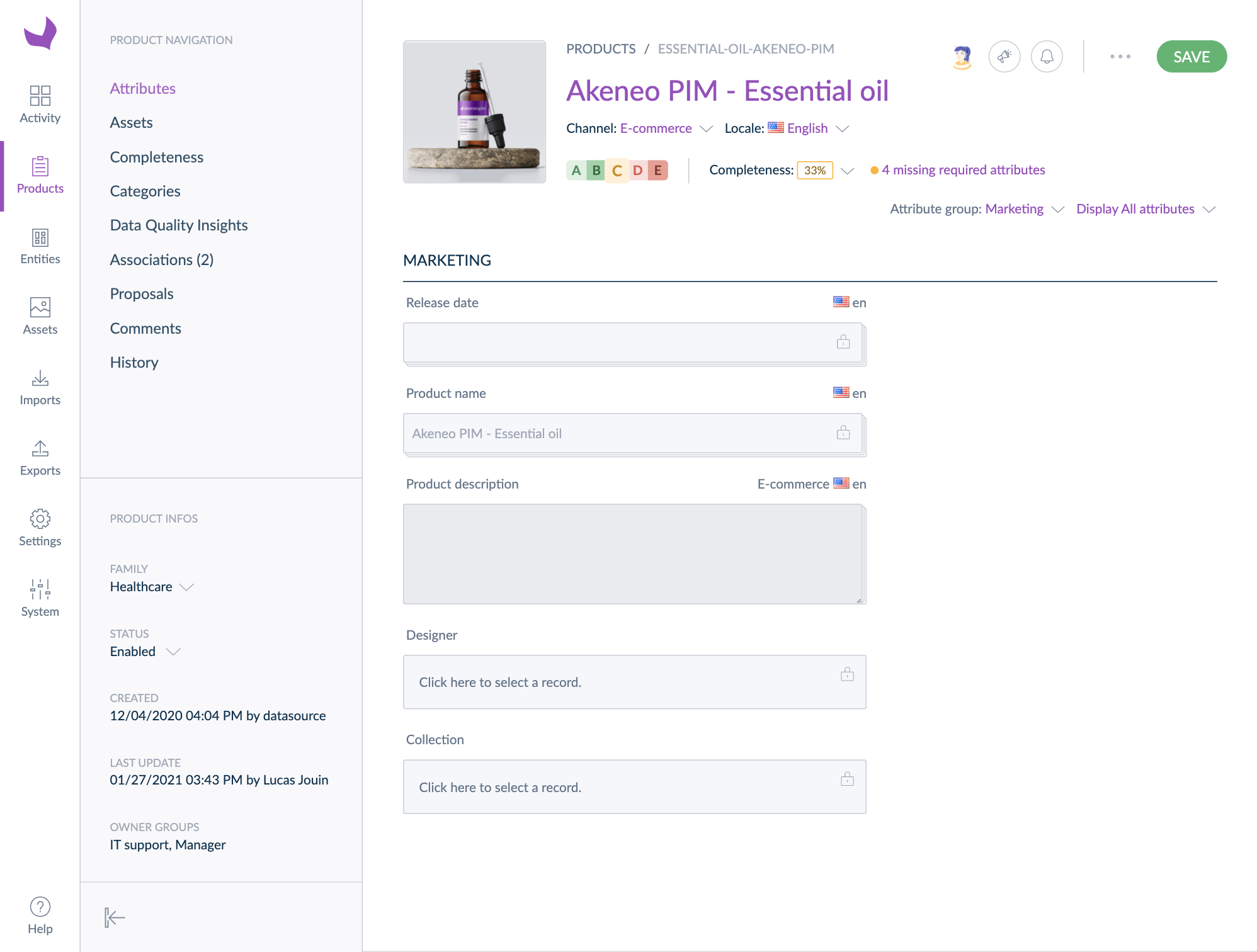
Mary is in the Purchase team user group that has no right on product information regarding the Marketing attribute group. As a result, in the product form, she cannot see at all neither the Marketing attribute group, nor its attributes, as you can see in the screenshot below.
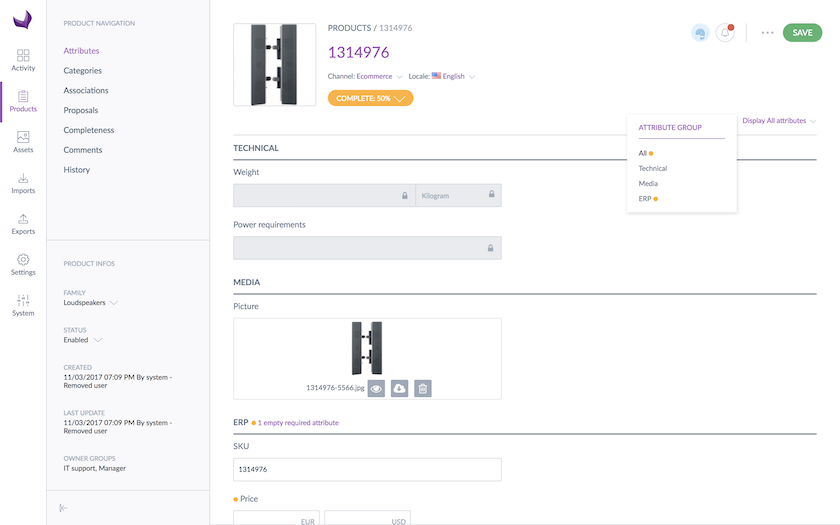
Set rights to user groups
So now you better understand how the rights depending on the attribute groups work, let's configure it in the interface:
- Go to Settings and click Attribute groups
- Select the attribute group in the grid
- Click the Permissions tab
- Click the fields to select the user groups entitled to the appropriate rights
- Click Save
The rights are immediately applied to the users.


