Definition of a category
In Akeneo, a category is used to classify products. A category is always part of a main category tree (or classification tree).
You can have one or more category trees in Akeneo with an unlimited number of levels (categories, subcategories, sub-subcategories...).
Learn more at Akeneo Akademy
Deepen your understanding of Categories in this interactive course.
Differences between families and categories
Categories
- Trees and categories are a way to classify your products
- A product can be in several or no categories
Families
- A family is a set of attributes used to enrich a product
- A product can only belong to one family
How to create a new category?
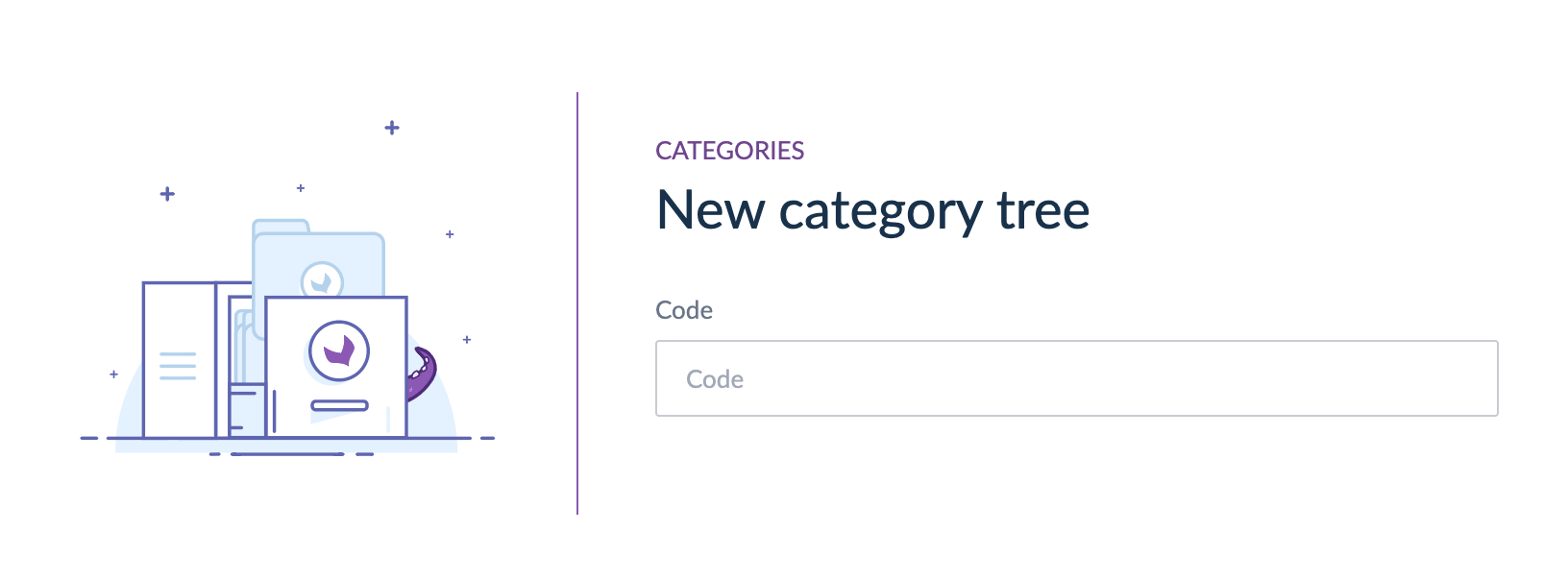
A category or a category tree only needs a code to be created. You can name your category or category tree and this name can be translated to any activated locale in the PIM.
From the user interface
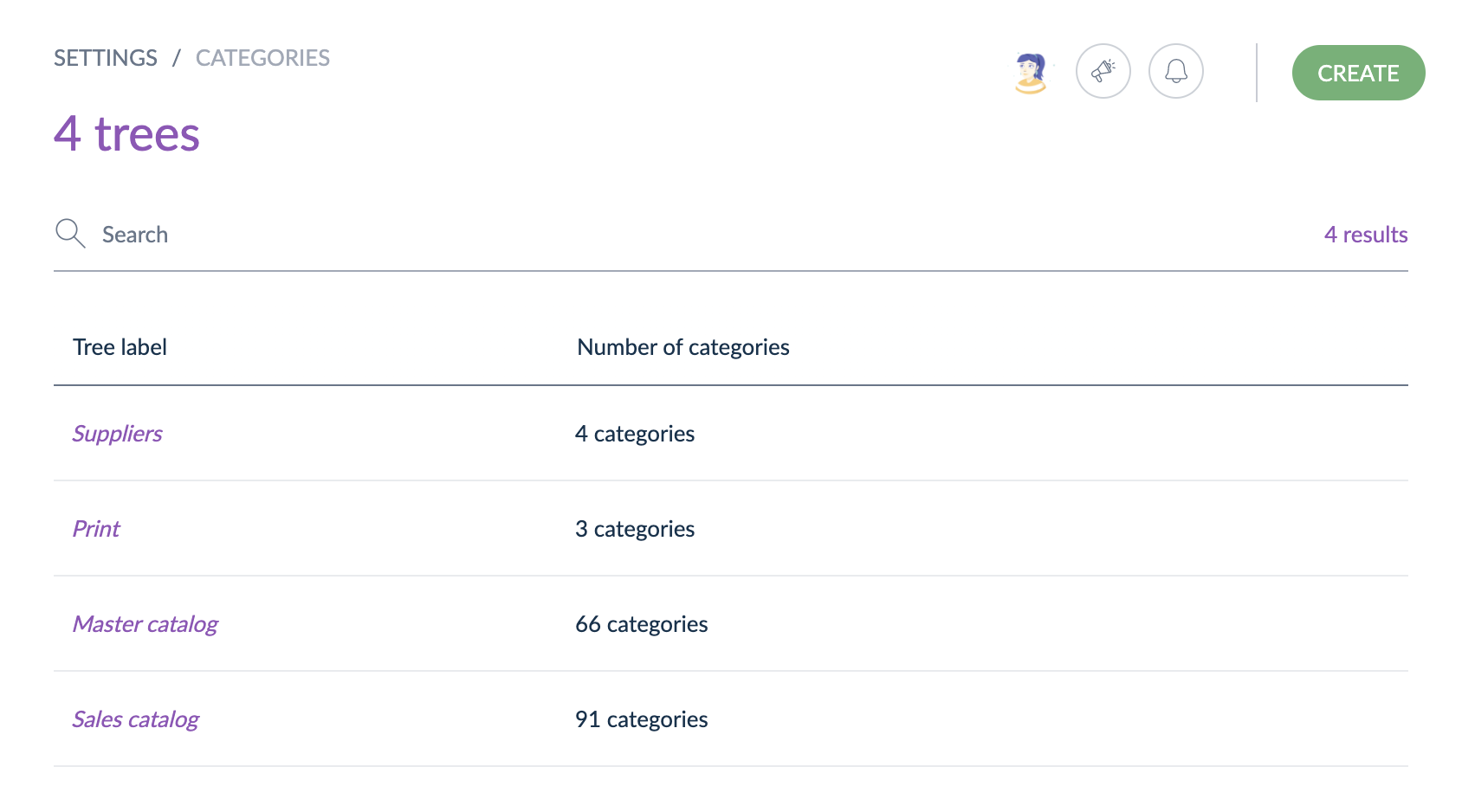
Go to Settings/Categories. To create a new category tree, click on Create button.

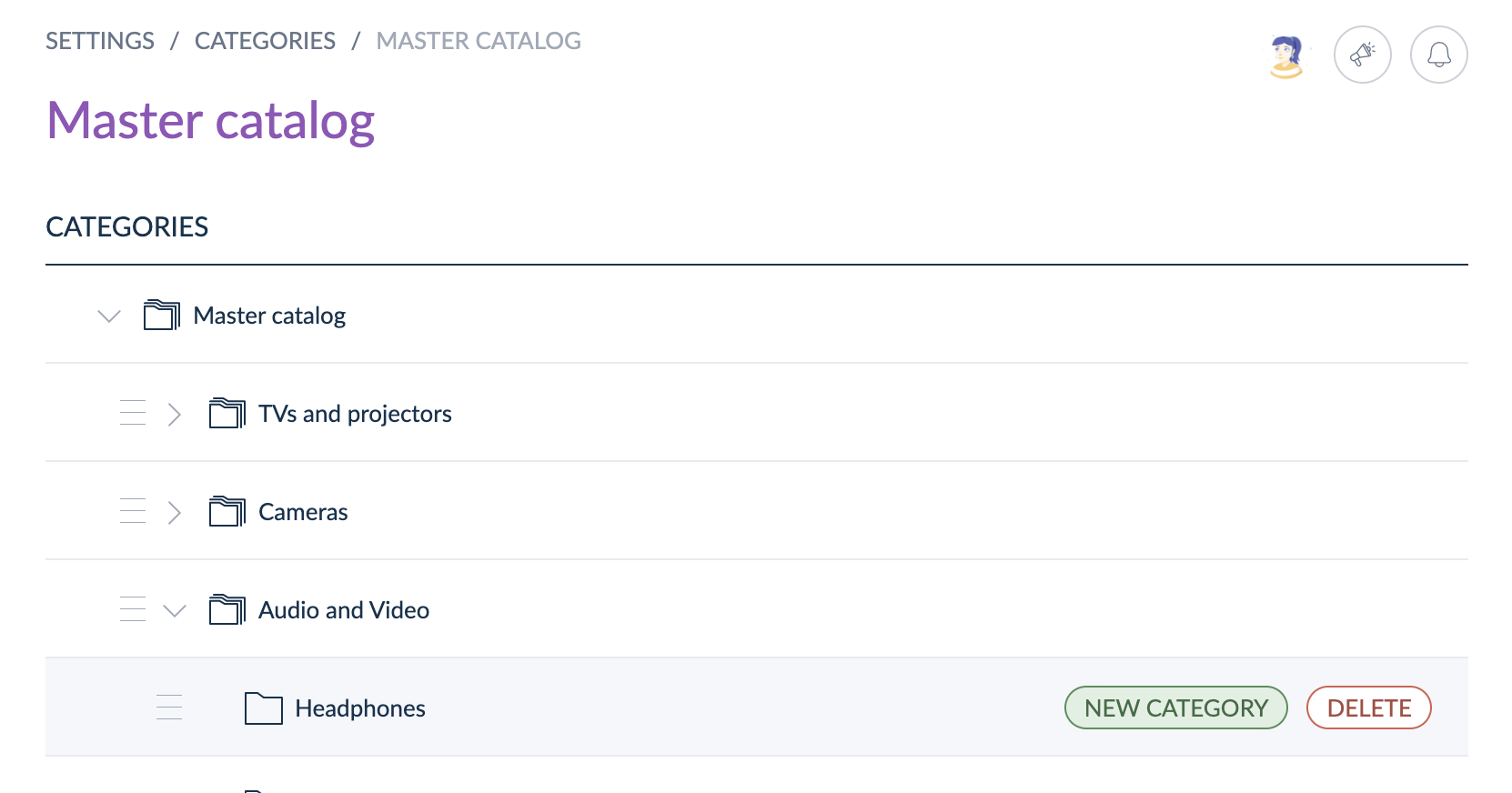
To add a new category or subcategory in this tree, select your tree in the list. Once the tree is selected, hover on the tree name to add a new category or on a category to add a new subcategory.
Through imports
Akeneo comes with import jobs that allow you to create or update category trees and categories. You can use them to create a new tree, update a category tree or a category labels, or add new categories or subcategories for instance.
To do so, use the search bar to find the existing job from Imports or click on Create Import Profile to add a new import. You can choose to use a CSV or XLSX import profile.
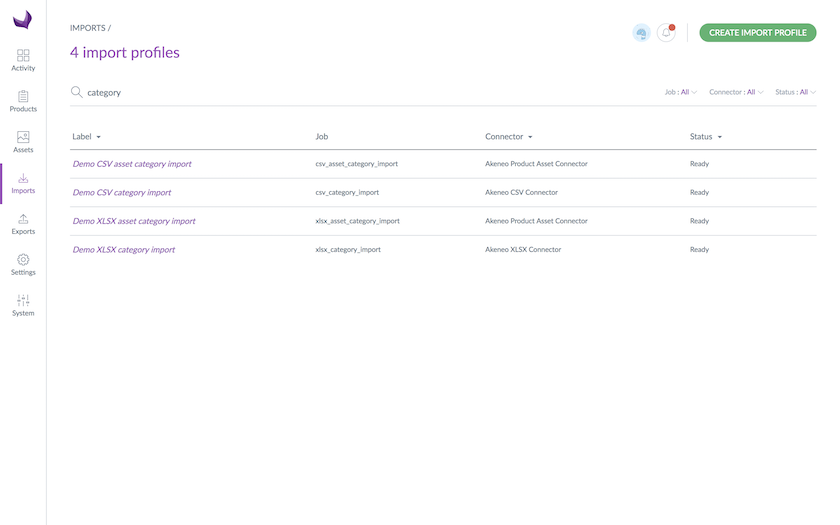
If you do not know the file format to import, go to Exports, use an existing XLSX or CSV category export profile (or create a new one) and use the exported file as a template!
To learn how to create/update a category through the API, see the API documentation.
Root category import
Please be aware that to prevent products from being assigned to a category tree via a rule, setting the category to a root category tree is not an option. Categorization needs to necessarily be done under a sub category.
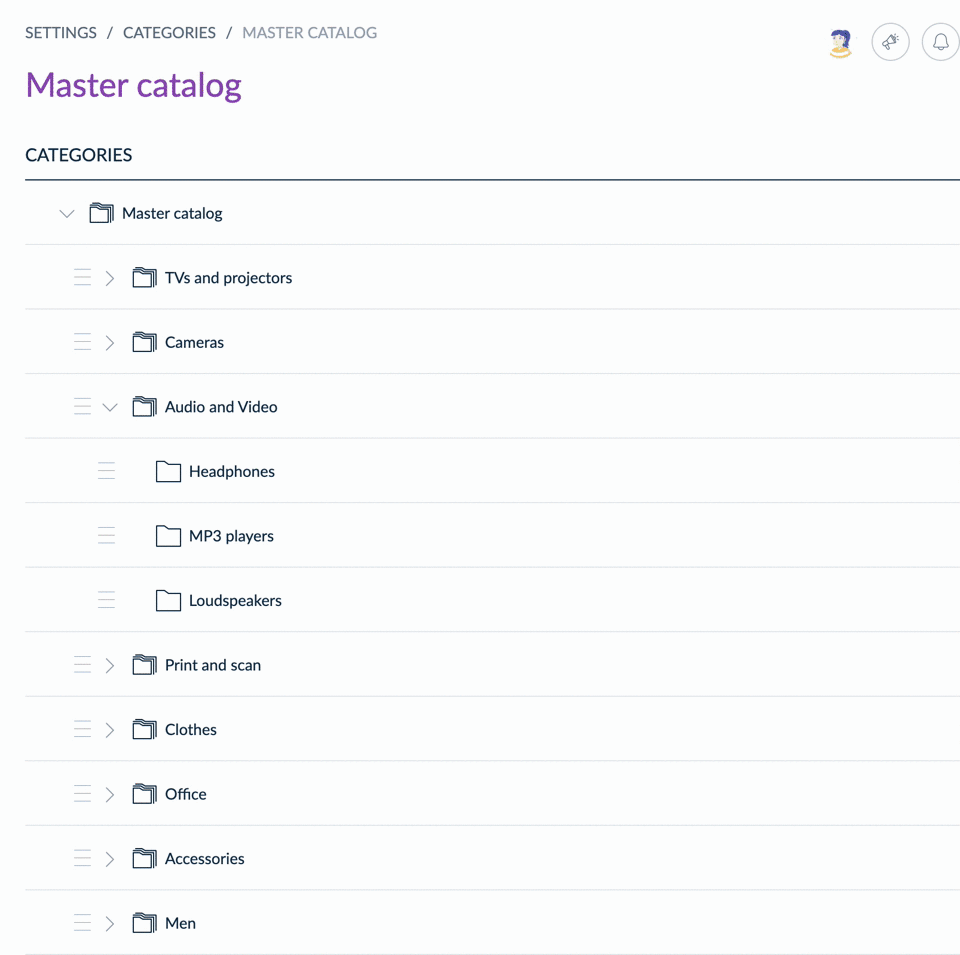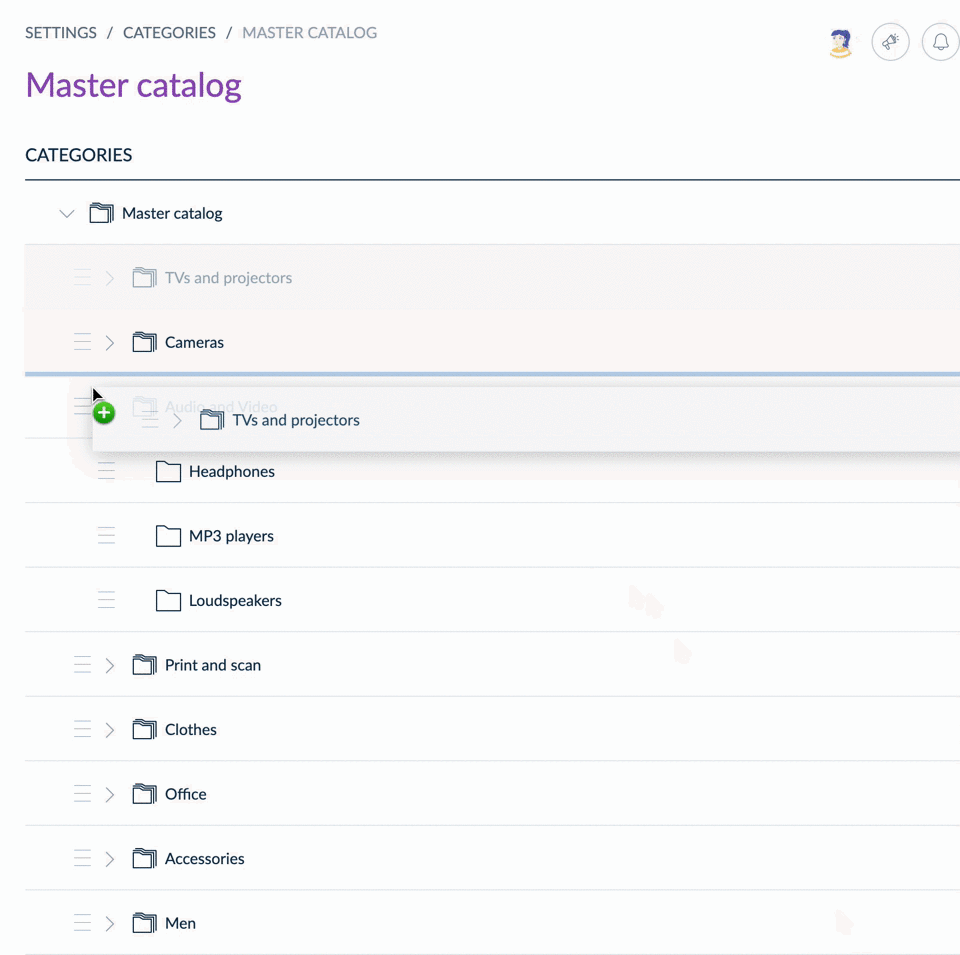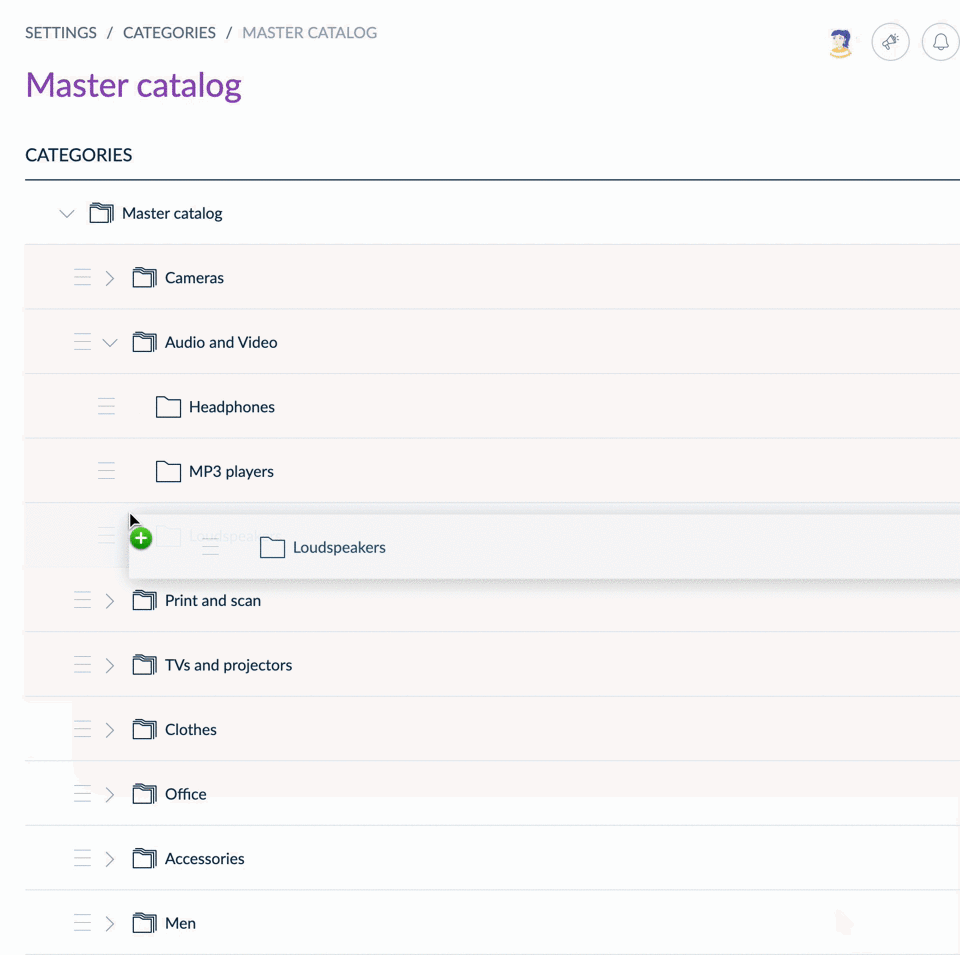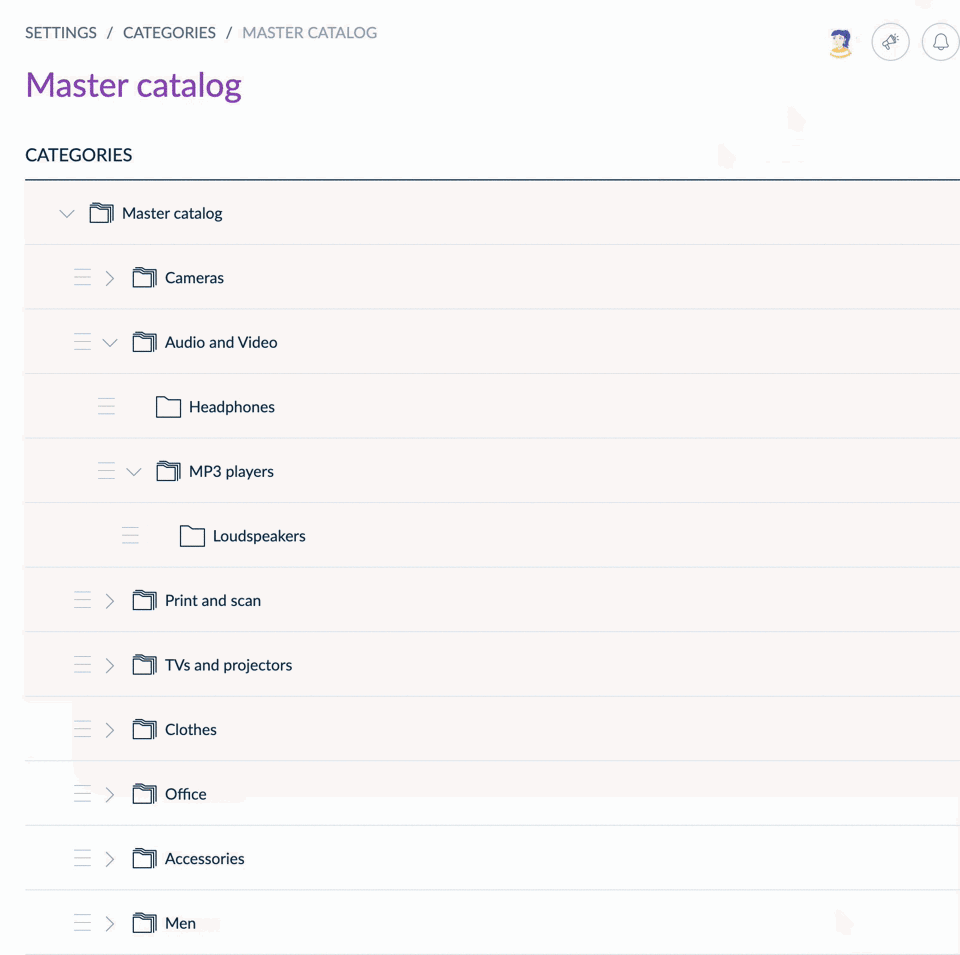
Sort categories
From the UI, you can drag & drop categories to reorder them within the tree.
If you do not have the permission to see the categories (which is a permission defined for your user role in System/Roles), you will not be able to access the category panel displayed on the left side of the screen and access to the Settings/Categories menu.
You cannot sort category trees only categories. Trees are displayed by date of creation: new trees are displayed first.
In the Enterprise Edition, you can define specific user rights on categories, to give ownership on products. For more information about permissions on categories see the following page: Set rights on your catalog.
Define category tree settings
You can configure these settings per category tree, allowing for flexibility if you use multiple trees for different purposes.
Required for Completeness
The "Required for Completeness" setting allows you to specify that a product's categorization within a particular category tree is required for a product to be complete for a given channel.
When a product lacks categories in a required category tree, this information will be clearly displayed in the completeness section of the Product Edit form.

Select the channels for which you want the categorization requirement to apply (by default, all channels linked to the category tree are selected).
- Products must be categorized within the required category tree; otherwise, their completeness on the relevant channel(s) will be affected.
- Only category trees can be marked as required for completeness, not individual child categories.
Setting a category tree as required for completeness triggers a completeness re-calculation for all products.
This is why this action is placed in the "danger zone" of the category tree editing form.
- Click on the “edit” button in the completeness section.
- Remove all the channels from the list.
- Save your action.

Mandatory category tree
This setting enforces that all products and product models must be categorized within at least one category of the selected category tree(s) upon creation or modification. This requirement is consistently applied across the user interface (UI), during imports, and via API.
You can designate several category trees as mandatory. In this case, a product or product model must have at least one category assigned from each of the mandatory trees.
When enabling this setting for the first time, ensure that all existing products and product models are already assigned to at least one category within the chosen tree(s). If not, you will be prompted to categorize them before you can save any changes.
Restrict categorization to the lowest level
This setting enforces a strict categorization hierarchy. When enabled, users can only assign products & product models to leaf categories – those at the very bottom of the tree, with no sub-categories beneath them. This prevents products from being assigned to broader, parent categories, ensuring that products are always classified with the most specific category available.
Example: Imagine a category tree like this:
- Electronics
- Televisions
- LCD TVs
- OLED TVs
- Audio
- Headphones
- Speakers
- Televisions
With "Allow category selection at the last level only" enabled, a product or product model could be assigned to "LCD TVs" or "OLED TVs" (leaf categories), but not to "Televisions" or "Electronics" (parent categories).
Before implementing this limitation, ensure all products and product models are assigned to leaf categories. Otherwise, you won't be able to save them.
Changing your category structure (e.g., adding a new level) may prevent you from saving products. Please review the impact on your products before proceeding.
Maximum Number of Categories per Product
This setting limits the number of categories a product or product model can be assigned to within a specific category tree. This is useful for preventing over-categorization and maintaining a clear, organized product catalog.
Example: If you set the maximum number of categories per product to 3, a product could be assigned to a maximum of three categories within that specific category tree. If a user attempts to add a fourth category, it will impossible to save the product.
Note that this limit will apply to the product models, sub product models, and product variants, and this limit will include inherited categories from parents.
Example:
Let's say you sell clothing and have a category tree like this:
- Clothing
- Men's
- Shirts
- T-Shirts
- Dress Shirts
- Pants
- Shirts
- Women's
- Dresses
- Skirts
- Men's
You set the maximum number of categories per product to 2.
- Product Model: You have a product model called "Classic T-Shirt." This model and all its variants (e.g., "Classic T-Shirt - Red," "Classic T-Shirt - Blue") are subject to the 2-category limit, including inherited categories. If the "Clothing" category is set to the product model, then all variants underneath automatically inherit that category. This means the "Classic T-Shirt" model and all its variants already have one category assigned ("Clothing") before any other assignments are made.
- Variant: A specific variant, "Classic T-Shirt - Red," could be assigned to "Shirts." Because the limit is 2 and "Clothing" is inherited, the variant is now at its maximum category count. It cannot also be assigned to "T-Shirts" or any other category.
How to categorize a product?
Learn more about product categorization on the following page: Categorize a product
A product can be categorized in none, one or several categories. An uncategorized product will not be exported.
category, categories, categoryId are used for internal purposes, you cannot use these words as "codes" in the PIM.
Set rights on categories
Learn more about user rights to see & edit products based on their categorization on the following page: Set rights on your catalog


